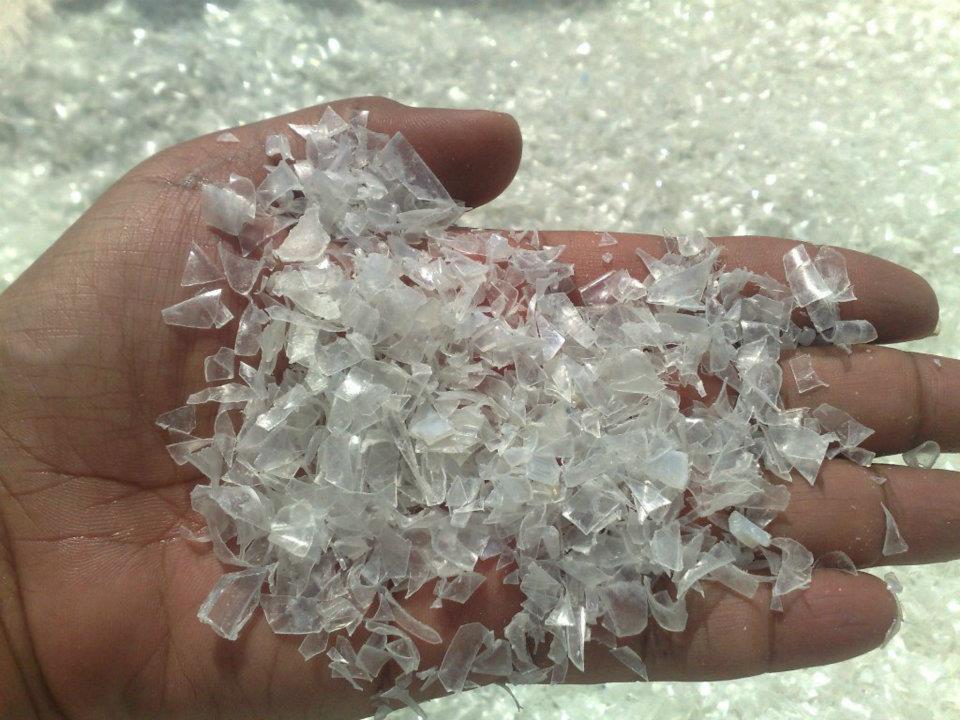
In India, a new wave of environmental consciousness is sweeping the nation as it embraces the circular economy, a sustainable approach to waste management. With its rapidly growing population and increasing consumption rates, waste management has become a pressing issue for India. However, instead of letting waste pile up or relying on traditional linear models of production and consumption, the country is taking proactive steps to break free from the waste cycle.

Through innovative solutions and government initiatives, India is redefining the way it handles waste. From recycling and upcycling to promoting responsible consumption, businesses and individuals are finding creative ways to turn waste into valuable resources. This shift towards a circular economy is not only helping to reduce pollution and conserve resources, but it is also creating new economic opportunities and improving the overall quality of life.
As more companies and individuals embrace the circular economy, India is paving the way for a greener and more sustainable future. Through effective waste management practices and a commitment to responsible consumption, India is proving that it is possible to break free from the cycle of waste and create a more sustainable and prosperous society.
The environmental impact of waste in India
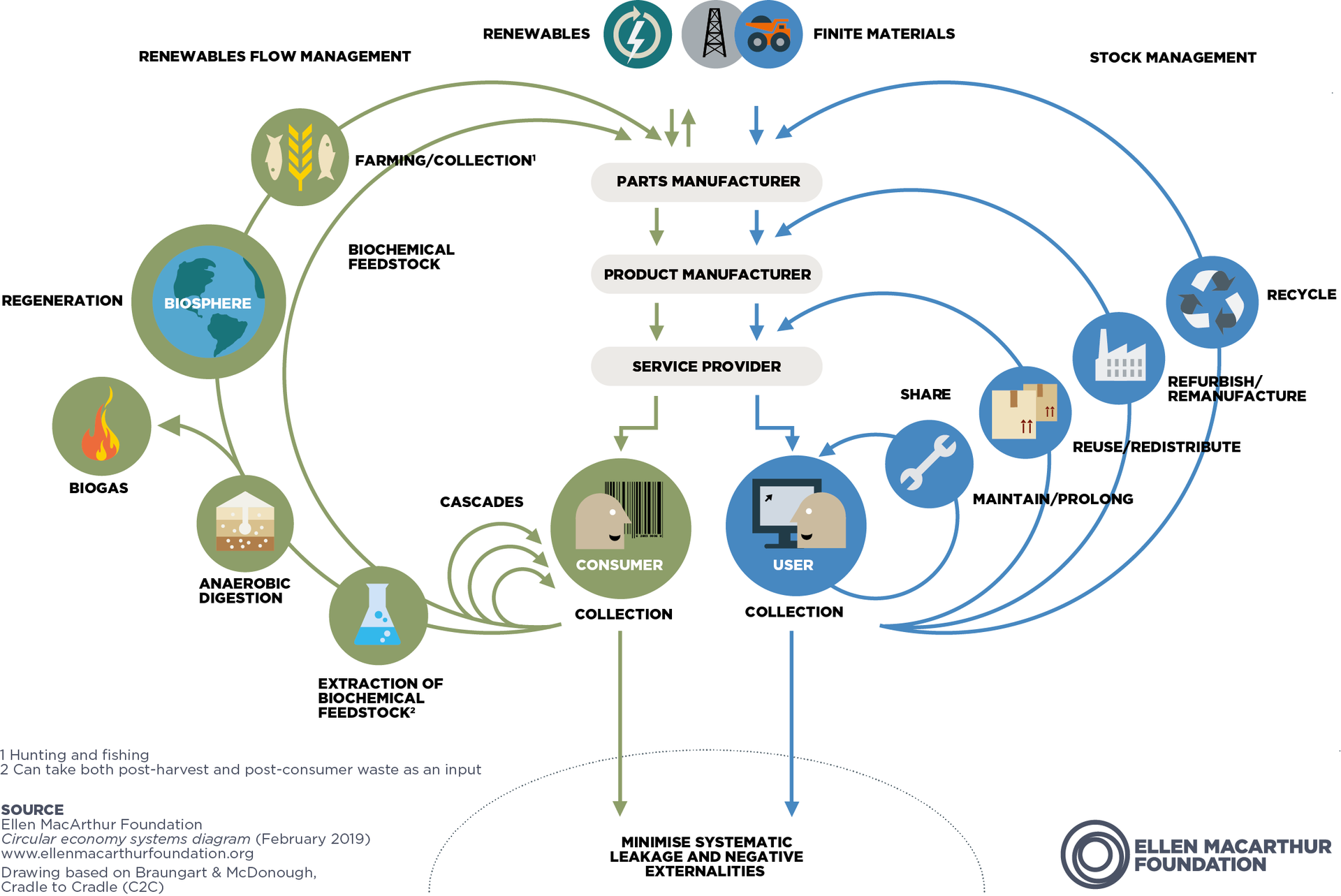
The circular economy is a concept that aims to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency. Unlike the traditional linear economy, which follows a "take-make-dispose" model, the circular economy promotes the reuse, recycling, and repurposing of materials. It is based on the principles of designing out waste and pollution, keeping products and materials in use for as long as possible, and regenerating natural systems.
In the context of waste management, the circular economy approach involves viewing waste as a valuable resource that can be utilized rather than discarded. It encourages the adoption of innovative technologies and practices that enable the recovery and regeneration of materials and resources. By closing the loop and creating a continuous cycle of production, consumption, and recycling, the circular economy minimizes the environmental impact of waste and reduces the reliance on finite resources.
The benefits of embracing the circular economy
India is home to over 1.3 billion people, making it the second-most populous country in the world. With such a large population, waste generation is a significant challenge. The improper disposal and management of waste have serious environmental consequences. Landfills are overflowing, rivers and water bodies are polluted, and air quality is deteriorating due to the burning of waste.
The impact of waste on the environment goes beyond just pollution. The extraction and production of raw materials for manufacturing products contribute to deforestation, habitat destruction, and climate change. Additionally, the energy consumed in the production and transportation of goods further exacerbates the carbon footprint.
Initiatives and policies promoting the circular economy in India
Embracing the circular economy offers numerous benefits for India. Firstly, it reduces the strain on natural resources by promoting resource efficiency and minimizing waste. This not only helps to conserve valuable resources but also reduces the environmental impact of resource extraction and production.
Secondly, adopting circular economy principles creates new economic opportunities. Recycling and upcycling industries can create jobs and stimulate economic growth. By tapping into the potential of waste as a resource, India can develop a circular economy that generates income and contributes to sustainable development.
Furthermore, the circular economy improves the overall quality of life. By reducing pollution and promoting responsible consumption, it creates a healthier and cleaner environment for all. The circular economy approach also encourages innovation and collaboration, leading to the development of sustainable technologies and solutions.
Swachh Bharat Abhiyan
(Clean India Mission)

The Indian government has recognized the importance of transitioning to a circular economy and has taken several initiatives to promote sustainable waste management. One such initiative is the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan (Clean India Mission), launched in 2014. This nationwide campaign aims to improve sanitation and cleanliness by focusing on waste segregation, recycling, and proper disposal.
The Extended Producer Responsibility framework (EPR)
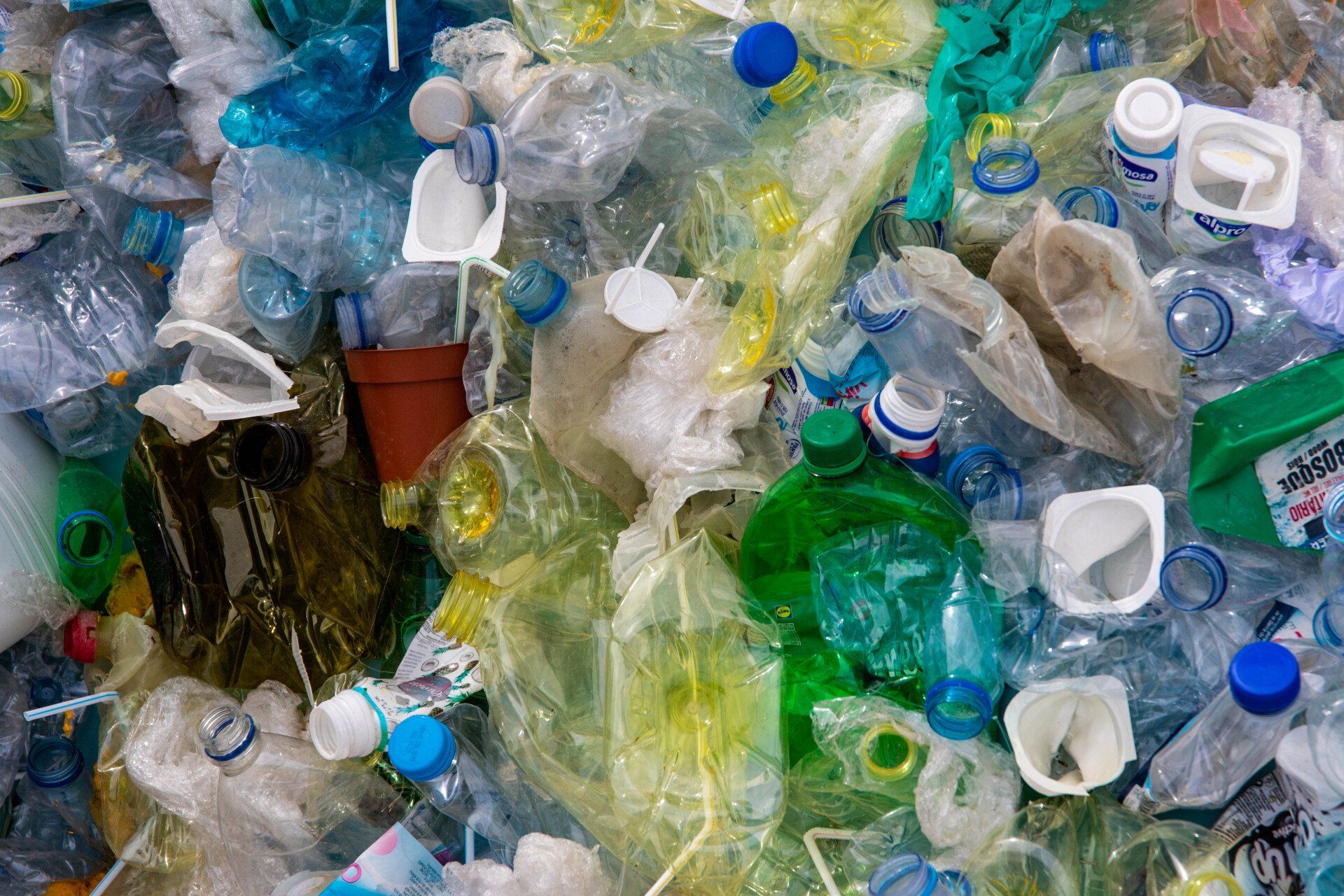

In addition to government initiatives, various policies and regulations have been implemented to encourage the circular economy. The Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) framework, for example, holds producers responsible for the end-of-life disposal of their products. This encourages manufacturers to design products with recyclability in mind and promotes the establishment of collection and recycling systems.
Challenges and obstacles to implementing the circular economy in India
Several organizations and businesses in India have already embraced the circular economy and are leading by example. One such case study is the recycling and upcycling company, Rimagined. They collect waste materials such as plastic and fabric scraps and transform them into unique and sustainable products. By creating a market for upcycled goods, Rimagined not only reduces waste but also supports local artisans and craftsmen.
Another success story is the Indian Railways' initiative to convert waste plastic into railway sleepers. By using waste plastic as a raw material, the railways reduce their reliance on timber and contribute to waste reduction. This innovative approach not only improves the durability and lifespan of railway sleepers but also reduces the environmental impact of the railways.
How businesses can transition to a circular economy model
While India is making significant progress in embracing the circular economy, several challenges and obstacles need to be addressed. One major challenge is the lack of awareness and education about the circular economy principles among the general public. Many people are still unaware of the environmental impact of waste and the potential of the circular economy to address these issues.
Another obstacle is the lack of infrastructure and facilities for proper waste management. Effective waste segregation, collection, and recycling systems need to be developed and implemented across the country. This requires investments in infrastructure, technology, and capacity building.
Additionally, the informal sector, which plays a significant role in waste management, needs to be integrated into the formal economy. Informal waste pickers and recyclers often work in unsafe conditions and are marginalized. By providing them with better working conditions and recognition, India can harness their expertise and contribute to the circular economy.

Consumer role in supporting the circular economy in India
Businesses play a crucial role in transitioning to a circular economy model. They can adopt sustainable production practices, such as using renewable energy and designing products for durability and recyclability. Implementing closed-loop supply chains and incorporating recycled materials into their products can also contribute to a circular economy.
Collaboration and partnerships between businesses, government agencies, and non-profit organizations are essential for promoting the circular economy. Knowledge sharing, research, and development of innovative technologies can accelerate the transition and create a supportive ecosystem.
Conclusion: India's journey towards a sustainable and waste-free future
The future prospects for the circular economy in India are promising. As the government continues to implement policies and initiatives, awareness about the circular economy is growing. More businesses are recognizing the economic and environmental benefits of adopting circular economy principles and are incorporating them into their strategies.
Furthermore, the circular economy has the potential to address other pressing issues, such as climate change and resource scarcity. By reducing waste and promoting sustainable practices, India can contribute to global efforts to mitigate climate change and achieve sustainable development goals.
At Aerofibre, we're committed to weaving a brighter future for our country through sustainable manufacturing practices. We are market leaders in rPET Flakes, rPET Sheets & Carpet Backing, and fully committed to sustainable manufacturing. Join us in promoting the use of rPET flakes and sheets in your products and promoting the adoption of circular economy in India.


Contact info
+91 9503111333
headoffice@aerofibre.com
102, 10th Floor, Maker Chamber VI, Jamnalal Bajaj Marg, Nariman Point, Mumbai - 400021
All Rights Reserved | AeroFibre
Join the Newsletter
We will get back to you as soon as possible
Please try again later
SDG Goals